Kenya’s real estate sector has become a cornerstone of the country’s economic growth. As urbanization accelerates and demand for housing, commercial spaces, and infrastructure increases, the real estate industry is playing an increasingly significant role in contributing to Kenya’s Gross Domestic Product. In this blog post, we explore how the real estate sector contributes to Kenya’s economy, its impact on employment, investment trends, and future potential.
Understanding GDP and Its Components
Before diving into the specifics of real estate’s contribution, let’s briefly define what GDP is. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures the total value of all goods and services produced within a country over a specific period. It includes four main components:
- Consumer Spending
- Investment
- Government Spending
- Net Exports
The real estate sector primarily falls under investment , particularly in construction, residential development, and commercial property investments.
How Real Estate Contributes to Kenya’s GDP
1. Direct Contribution through Construction and Development
According to data from the Kenya National Bureau of Statistics- KNBS, the construction sector contributes approximately 6-8% of Kenya’s GDP annually , with real estate being a major driver. This includes:
- Residential housing projects
- Commercial buildings– offices, malls, hotels
- Industrial parks and warehouses
- Infrastructure projects such as roads, railways, and utilities
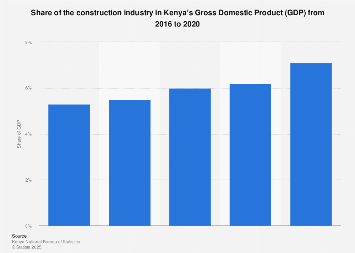
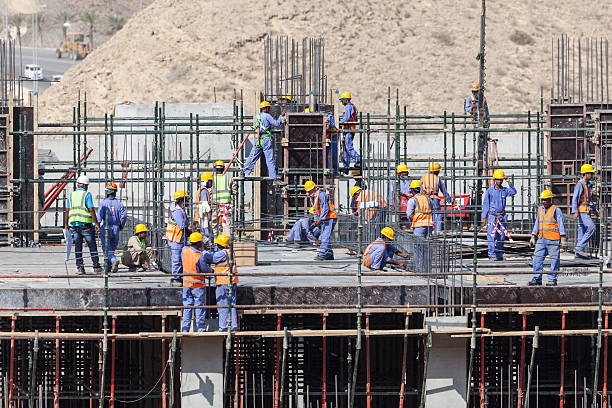
2. Employment Generation
Real estate is one of the largest employers in Kenya, providing jobs directly and indirectly across various sectors:
- Skilled labor- architects, engineers, surveyors
- Unskilled labor- masons, carpenters, site workers
- Sales and marketing professionals
- Property management and maintenance staff
It’s estimated that the sector employs over 2 million Kenyans , significantly reducing unemployment and boosting household incomes.

3. Attracting Foreign Direct Investment- FDI
Kenya’s real estate market has attracted considerable foreign direct investment, especially in Nairobi, Mombasa, and Kisumu. International developers, private equity firms, and multinational corporations are investing heavily in mixed-use developments, affordable housing, and luxury apartments.
In 2024 alone, FDI inflows into the real estate and construction sector reached KSh 45 billion , according to the Central Bank of Kenya.

4. Affordable Housing Programs and Government Initiatives
The Kenyan government has launched several initiatives aimed at addressing the housing deficit, including:
- Affordable Housing Program- AHP
- Nawiri Homes
- Mortgage-backed securities framework
These programs not only provide homes but also stimulate economic activity through procurement of materials, creation of jobs, and increased consumer spending.

5. Linkage Effects on Other Sectors
The real estate sector acts as a multiplier, stimulating growth in other industries such as:
- Cement and steel manufacturing
- Furniture and interior design
- Transport and logistics
- Banking and finance- mortgages, insurance
This interdependence strengthens the broader economy and ensures sustained GDP growth.
Challenges Facing the Sector
Despite its promising growth, the real estate sector in Kenya faces several challenges:
- High cost of land and financing
- Bureaucratic delays in approvals
- Land ownership disputes
- Informal settlements and lack of proper planning
Addressing these issues requires coordinated efforts between the government, private sector, and civil society.
Future Outlook
Kenya’s real estate sector is poised for continued growth due to:
- Rapid urbanization- urban population expected to reach 50% by 2030
- Technological innovations e.g., smart cities, green buildings
- Youth-driven entrepreneurship in real estate tech- PropTech
- Increased access to mortgage financing through digital platforms
With the right policies and investments, the real estate sector could contribute up to 10-12% of GDP by 2030.
Conclusion
The real estate sector in Kenya is more than just bricks and mortar — it’s a powerful engine driving economic transformation. From job creation to attracting global capital, real estate plays a vital role in shaping Kenya’s economic landscape. As the nation continues to grow and develop, fostering a robust and inclusive real estate market will be key to sustaining long-term economic prosperity.
