The Structure of Kenya’s Real Estate Market
Kenya’s real estate market is divided into several key categories:
- Residential: Homes, apartments, and townhouses
- Commercial: Offices, retail spaces, and hotels
- Industrial: Warehouses, factories, and logistics centers
- Land: Agricultural, residential, and investment plots
Each segment has its own demand drivers and investment potential. Nairobi remains the most developed and competitive market, followed by Mombasa, Kisumu, Nakuru, and Eldoret.

Key Players in the Kenyan Real Estate Sector
Several stakeholders contribute to how real estate works in Kenya:
1. Developers
Companies that build residential and commercial properties, such as:
- Centum RE
- East African Portland Cement Company (EAPCC)
- Knight Frank Kenya
2. Buyers & Investors
Both individuals and institutions investing in property for personal use or returns.
3. Real Estate Agents
Licensed professionals who help buyers and sellers find or list properties.
4. Banks & Mortgage Institutions
Offer financing options for property purchases. Major players include:
- Housing Finance Bank
- Co-operative Bank
- Stanbic Bank
5. Government Agencies
Oversee land registration and regulation:
- Registrar of Titles
- National Land Commission (NLC)
- Survey of Kenya

Understanding Property Ownership in Kenya
There are two main types of property ownership in Kenya:
1. Freehold Ownership
- Full ownership of land and buildings
- Available only to Kenyan citizens
- Offers permanent rights and can be passed on through inheritance
2. Leasehold Ownership
- Right to use land for a specified period (usually 33, 44, or 99 years)
- Open to both citizens and foreigners
- Can be renewed upon expiration depending on government policy
It’s important to verify the type of title deed before purchasing any property.
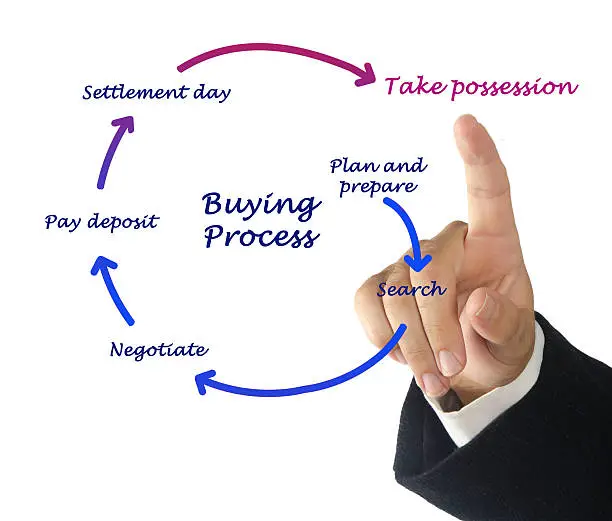
The Real Estate Buying Process in Kenya
Buying property in Kenya involves several steps:
Step 1: Find a Property
Use platforms like Realestate.co.ke, Jengo Homes, or work with a licensed agent.
Step 2: Conduct Due Diligence
Verify ownership documents, check for encumbrances, and ensure clear title.
Step 3: Sign a Sale Agreement
A preliminary agreement outlining terms and conditions of sale.
Step 4: Pay Deposit
Typically 10% of the total price.
Step 5: Apply for Transfer
Submit forms at the Lands Office and pay stamp duty and registration fees.
Step 6: Wait for Registration
The process usually takes 3–6 months after submitting all documents.
Legal Framework and Documentation
Legal compliance is crucial in real estate transactions in Kenya.
Important Documents:
- Title Deed – Proof of ownership
- Survey Map – Shows boundaries and size
- Rate Clearance Certificate – Confirms no arrears in land rates
- Encumbrance Certificate – Verifies if the property is under mortgage or dispute
Always involve a licensed conveyance lawyer to handle the documentation and ensure legality.
Financing Real Estate in Kenya
There are several ways to fund your property purchase:
1. Personal Savings
Ideal for small-scale investors who want full control and avoid debt.
2. Mortgages
Available from major banks with interest rates between 9% and 16%. You’ll typically need:
- Proof of income
- Good credit history
- Down payment of 10%–30%
3. Crowdfunding Platforms
Emerging platforms like Jamii Housing allow group investments.
4. Partnerships
Investing with others helps reduce individual financial burden.
Rental Market and Returns
Kenya offers strong rental yields, especially in urban areas.
Average Monthly Rents (as of 2025):
- Nairobi:
- Studio apartment: KES 15,000 – 25,000
- 2-bedroom apartment: KES 30,000 – 50,000
- Mombasa:
- 1-bedroom flat: KES 12,000 – 20,000
- Kisumu:
- Single room: KES 5,000 – 8,000
Property management companies can help with tenant screening, rent collection, and maintenance.
Common Challenges in Kenyan Real Estate
Despite its potential, real estate in Kenya comes with challenges:
- High upfront costs
- Lengthy registration process
- Unclear land titles and disputes
- Lack of transparency in some transactions
- Inconsistent enforcement of property laws
Doing thorough research and working with professionals can help mitigate these issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can foreigners own property in Kenya?
Foreigners cannot own land on a freehold basis but can lease it for up to 99 years.
What is the average cost of a house in Kenya?
Prices vary by location. In Nairobi, a 2-bedroom apartment ranges from KES 3 million to over KES 10 million.
Is real estate a good investment in Kenya?
Yes, especially in high-demand areas where rental yields and appreciation rates are favorable.
Conclusion
Understanding how real estate works in Kenya is the first step toward successful property investment. From knowing the legal framework to navigating the buying process and exploring financing options, this guide gives you the foundation needed to make smart, informed decisions.
Whether you’re a first-time buyer or expanding your portfolio, Kenya’s real estate market offers promising opportunities — provided you approach it with knowledge and strategy.
